A brief Introduction
I will be starting a little Oracle RAC series with VMware and will be fondly calling it “RACing ahead with Oracle on VMware.” This first part is intended to give you a brief introduction to setting up VMware and the importance of other tools such as VNC, freeNX or NoMachine, PuTTY, etc. I hope that you will enjoy reading these articles (and hopefully start playing with it) as much as I will enjoy writing them (while playing with them).
You want to run Oracle on multiple platforms? You want to be able to install once and then go ahead and play with the database after having set it up once and not need to reinstall the software (especially on various distro’s of Linux where OS installations could take a toll on your motivation?) With the introduction of OPS and from Oracle 9i onwards RAC (Real Application Clusters), you are very curious to learn these newer technologies, you want to watch and learn how RAC works but unfortunately you just have one computer at home. Even at work it’s not just that easy to get a couple of machines , if not servers, to hook them up, build clusters and have them all shared Cooked or RAW via a SCSI let alone JBOD, SAN or NAS.
Fortunately there is an answer to your (our) prayers. Thanks to VMware, you have a technology that offers virtualization. I began using VMware a couple of years back. It started with a mere curiosity to experiment on other Operating Systems and soon enough I had Oracle 8.1.7 installed on Redhat 8.0. It was fun to see Oracle run and behave differently on a totally different OS and without damaging my current Windows installation. I also tried my hand a dual boot (using PartitionMagic 8.0) but it was way too complicated. There are however other products like Microsoft Virtual Server but we will stick to VMware as it supports various OS’s such as Fedora, RHEL, SuSe, Solaris (still experimental though), Windows. Check out this comparison of several Virtual machines if you are further interested.
Virtualization
So what is Virtualization? And how does VMware workstation help us achieve this? Well, it is pretty simple. You just build up Virtual machines (Guest OS) on top of your Host Operating System. This machine is a typical X86 machine, having its own set of CPU, Memory (which you can re-adjust even after having created the virtual OS), Hard Disk, network cards, floppy drive and CD-ROM. For more about Virtualization I suggest you read this excellent article (which also got slashdotted!)
The advantages of Virtualization are rather clear.
- Easy configuration (as well see later)
- Manageable (Moving, backup, restore etc)
- Simulation and Isolation : Copy and recreate your ADS/LDAP/DNS servers and create own networks
- Excellent means to demonstrate things like Oracle RAC, Workload testing etc. before deploying it in production
So, as you can see, this is a powerful tool for developers, testers, consultants or just about anyone. ( In fact, virtualization goes a lot farther than this and you can achieve Server Consolidation by creating several under utilized Servers in one physical machine, but as I said, we won’t get too much into it as our goal is to set up Oracle RAC on VMware and play with several RAC related scenarios on our *Desktop Datacenter*).
Where to get VMware Workstation
You can simply go to the VMware Site and get yourself a 30 day fully functional trial license. However, it is a really a product you would want to consider buying. Imagine the power of running all kinds of scenarios on just one laptop!
Getting VNC viewer and/or freeNX NoMachine
You will occasionally need to set up remote connections to your server–VNC and NoMachine come to my mind as possible candidates. Both of these products help achieve remote desktop connectivity. Although the freeNX product promises a better and faster, user experience than VNC and it goes very well with SSHD, which is a good thing. You can get VNC viewer and/or freeNX here.
Getting PuTTY
You will need a SSH connection to your database server. I suggest that you do not do telnet. PuTTY is ideal for Windows client and you can get it here.
Now that we know what we can achieve through a Virtual Machine, and the usage of tools such as VNC or freeNX, PuTTY, or SSH,let’s get started by installing VMware and then creating an empty Virtual Machine in it.
Installing VMware and creating an empty Windows 2003 Skeleton
We will assume that installing VMware is not going to be a problem so we will move quickly to the other part of creating a Virtual Machine.
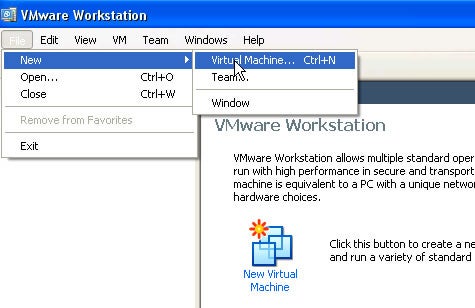
Step 1: Choose New>Virtual Machine
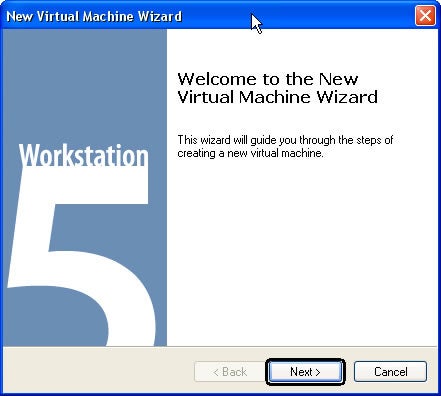
Step 2: Next
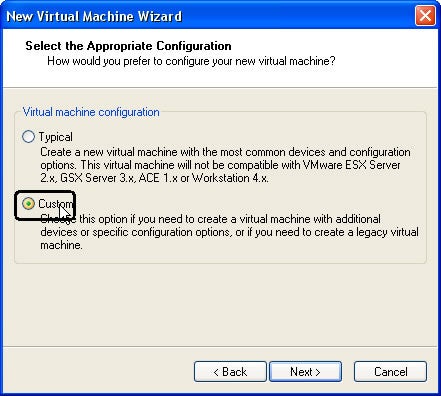
Step 3: Custom
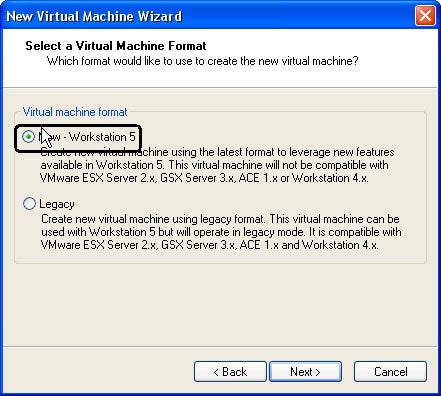
Step 4: New Workstation 5
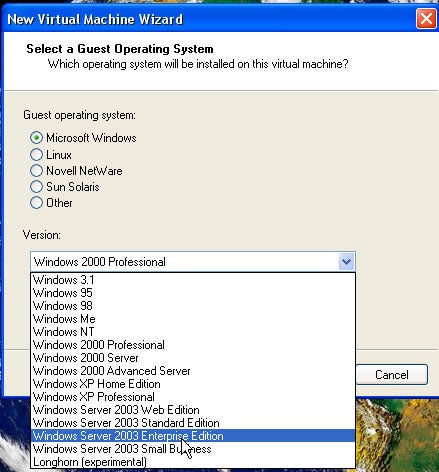
Step 5: Microsoft Windows> 2003 Enterprise Edition
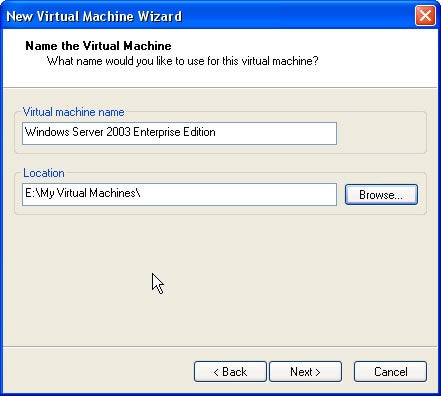
Step 6: I prefer NOT to install it under C:\
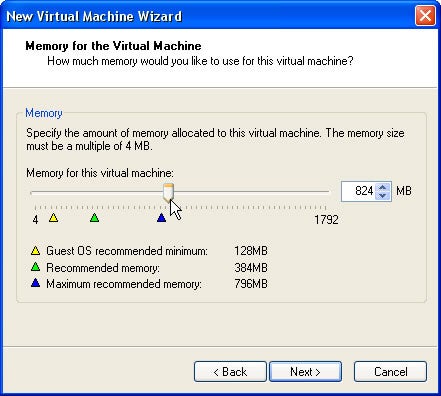
Step 7: Here I have 1G memory and 800 MB odd memory is fine given that we will do some RAC work here